mirror formula class 10 previous year questions

A mirror is a transparent glass with a very thin reflective layer, and the back side of the glass opposite the incident is painted. A mirror forms the image of any object positioned in front of it by reflection. The incident light ray, also known as reflected ray, coming from the object gets reflected back. These reflected rays of light converge to form an image, and the generated image will be a real image
FOR MORE THAN 100 QUESTIONS DOWNLOAD THE PDF.
mirror formula class 10 previous year questions

1) Convex Mirror
2) Concave Mirror
The mirror equation or mirror formula is the relation between the object’s distance from the mirror, the focal length of the mirror and the distance of the image from the mirror.
1/f=1/v+1/u
Where,f = focal length of the spherical mirror
v = the distance between image and mirror
u = the distance between object and mirror
mirror formula class 10 previous year questions
Q.1.)Write down four important characteristics of image
formed by a plane mirror.
Ans : [CBSE 2014]
Image is virtual, erect, laterally inverted and of same
size as object.
Q.2.) Describe a spherical mirror.
Ans : [CBSE 2014]
Spherical mirror is a part of a sphere. If reflection takes place from inside, it is said to be concave mirror,and if the reflection takes place from outside surface.
Q.3.) Define the following terms in relation to concave spherical mirror:
a. Pole
b. Centre of curvature
c. Radius of curvature
d. Principal axis
e. Principal focus
f. Aperture
g. Focal length (each one mark)
Ans : [CBSE2013, 2014, 2015]
a. The mid point of mirror is known as pole.
b. The centre of curvature of a spherical mirror is
the centre of that sphere of which mirror is a part,
c. The distance between pole and centre of curvature
is called radius of curvature of the mirror.
d. The straight line joining the pole and centre of
curvature is called principal axis.
e. The point on the principal axis through which
parallel rays to the principal axis passes or appear
to pass after reflection.
f. The diameter of the mirror or size of the mirror is
called aperture.
g. The distance between focus and pole of a mirror
is the focal length of the mirror.
Q4). What is the radius of curvature of a plane mirror?
Ans : [CBSE 2015]
The radius of curvature of a plane mirror is infinite.
Q.5). How many images are formed by two parallel mirrors?
Ans : [CBSE 2015]
The images formed by two parallel plane mirrors will
be infinite.
Q6). Name a mirror that can give an erect and enlarged
image of an object.
Ans : [CBSE 2011, 2012, 2013]
Concave mirror
Q7). The radius of curvature of a spherical mirror is 20 cm.
What is its focal length?
Ans : [CBSE 2011]
Focal length f = R/2
f=20/2 =10cm
mirror formula class 10 previous year questions
Q.8)Define principal focus of a spherical mirror.
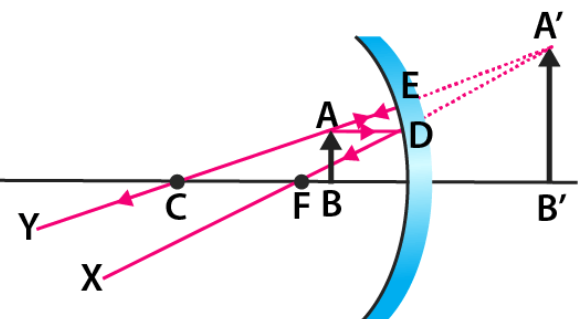
(b) For what position of the object does a concave
mirror form a real, inverted and diminished image
of the object? Draw the ray diagram.
(c) An object 4 cm high is placed at a distance of 6
cm in front of a concave mirror of focal length 12
cm. Find the position of the image formed.
Ans : [All India 2011]
a. The point on the principal axis at which the light
rays parallel to principal axis after reflection from
a concave mirror actually meet or appear to come
from in convex mirror on the principal axis is
called principal focus.
b. In case of a concave mirror, when the object is
placed beyond 2F(C) then image formed is real,
inverted and diminished

THE END THANK YOU

This online pharmacy offers an extensive variety of medications at affordable prices.
Shoppers will encounter both prescription and over-the-counter medicines to meet your health needs.
We work hard to offer safe and effective medications without breaking the bank.
Speedy and secure shipping provides that your order gets to you quickly.
Take advantage of ordering medications online with us.
priligy information
This website, you can discover lots of slot machines from leading developers.
Players can enjoy classic slots as well as modern video slots with high-quality visuals and interactive gameplay.
Even if you’re new or a seasoned gamer, there’s always a slot to match your mood.
play casino
All slot machines are available 24/7 and designed for PCs and mobile devices alike.
No download is required, so you can get started without hassle.
Platform layout is user-friendly, making it convenient to explore new games.
Register now, and enjoy the thrill of casino games!