Types of Chemical Reactions Class 10:
Chemical Reaction:-

In chemical reactions rearrangement of atoms takes place and new componds are formed with new properties.Those compounds takes parts in chemical reactions is called reactans and the formed compounds are called products.
Zn + CuSO4 → ZnSO4 + Cu
In this reaction Zn + CuSO4 is called reactants and ZnSO4 + Cu is called products.
Different Types of Chemical Reactions
Chemical reactions are of many types. Here, we are covering the most common eight types of chemical reactions, which are part of the class X chemistry syllabus as well
-
Decomposition reaction
-
Combination reaction
-
Combustion reaction
-
Neutralization reaction
-
Single displacement reaction
-
Double displacement reaction
-
Precipitation reaction
- Redox reaction (1)Decomposition reaction :-
-
In a decomposition reaction, molecules or compounds break down into two or more than two simpler chemically new substances. For example, electrolysis of water. In the electrolysis of water, water breaks down into hydrogen and oxygen, which show completely different properties than water.
2H2O (electricity) → 2H2 + O2
(2)Combination reaction :-
-
In a combination reaction, two or more molecules are combined together chemically to form a new substance (compound). Combination and decomposition reactions are opposite of each other. For example, when we burn magnesium ribbon (or magnesium), it gives grey-black ash of magnesium oxide.
2 Mg + O2 → 2MgO
(3)Combustion Reaction: – It is an exothermic chemical reaction that releases energy, generally in the form of heat. It is a reaction between fuel and an oxidant (generally atmospheric oxygen) that produces smoke, water and heat generally. For example, when we burn methane, it gives carbon dioxide and water.
CH4 + 2O2 → CO2 + 2H2O
(4) Neutralization Reaction – In these reactions, acid and base react with each other and form salt and water. For example, hydrochloric acid reacts with sodium hydroxide (base) and forms sodium chloride (salt) and water. HCl + NaOH → NaCl + H2O (5) Single displacement reaction :- In these reactions, more reactive metal displaces less reactive metal from its salt. In these reactions, products can be determined through reactivity series. Reactivity series is a series in which elements are arranged in decreasing order of their reactivity. It means the elements present at the top of this reactivity series are more reactive than the elements present at the bottom. CuSO4 + Zn → ZnSO4 + Cu
The reaction of potassium with magnesium chloride is an example of a single displacement reaction. In this reaction, potassium displaces magnesium from its salt because potassium is more reactive than magnesium. Potassium is present at the top of the reactivity series and is the most reactive element.
2K + MgCl2 → 2KCl + Mg
Electrochemical Series:- Reactivty of elemnts given below.
Element
Electrode Reaction (Reduction)
Standard Electrode Reduction Potential E° (in volt)
Li
Li+ + e– → Li
-3.05
K
K+ + e– → K
-2.925
Ca
Ca2+ + 2e– → Ca
-2.87
Na
Na+ + e– → Na
-2.714
Mg
Mg2+ + 2e– → Mg
-2.37
Al
Al3+ + 3e– → Al
-1.66
Zn
Zn2+ + 2e– → Zn
-0.7628
Cr
Cr3+ + 3e– → Cr
-0.74
Fe
Fe2+ + 2e– → Fe
-0.44
Cd
Cd2+ + 2e– → Cd
-0.403
Ni
Ni+ + 2e– → Ni
-0.25
Sn
Sn2+ + 2e– → Sn
-0.14
H2
2H+ + 2e– → H2
0.00 (Standard)
Cu
Cu2+ + 2e– → Cu
+0.337
I2
I2 + 2e– → 2I–
+0.535
Ag
Ag+ + e– → Ag
+0.799
Hg
Hg2+ + 2e– → Hg
+0.885
Br2
Br2 + 2e– → 2Br–
+1.08
Cl2
Cl2 + 2e– → 2Cl–
+1.36
Au
Au3+ + 3e– → Au
+1.50
F2
F2 + 2e– → 2F–
+2.87
Note:-
- The negative sign of standard reduction potential indicates that an electrode when joined with SHE acts as an anode and oxidation occurs on this electrode.
-
Similarly, the +ve sign of standard reduction potential indicates that the electrode when joined with SHE acts as a cathode and reduction occurs on this electrode.
-
(6) Double displacement reaction :-
-
In these reactions, two aqueous ionic compounds exchange their ions (mostly cations) and produce two new compounds. For example, potassium nitrate reacts with aluminium chloride and forms aluminium nitrate and potassium chloride.
3KNO3 + AlCl3 ↔️ Al(NO3)3 + 3KCl
(7) Precipitation reaction :-
-
In these reactions, an insoluble precipitate is formed. In precipitation reactions, two soluble salts in aqueous solutions are combined and form an insoluble precipitate.
AgNO3(aq) + KCl(aq) ↔️ AgCl(↓ )+ KNO3(aq)
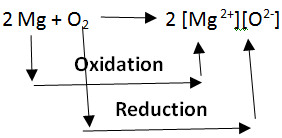
(8) Redox reaction :-
-
Those chemical reactions in which oxidation and reduction take place simultaneously are called redox reactions. Oxidation is the addition of oxygen, while reduction is the addition of hydrogen (or removal of oxygen). We have already discussed oxidation and reduction in a separate article with the title ‘Oxidation and Reduction’. You can refer to this article for a detailed explanation of oxidation and reduction. The reaction of copper oxide with hydrogen is an example of a redox reaction. In this reaction, hydrogen has undergone oxidation by gaining oxygen atoms while copper oxide has undergone reduction by removing oxygen.
List of Common Chemical Reactions
We are giving here a general list of common chemical reactions.
|
S.No. |
Chemical reaction |
Equation |
|
|
Electrolysis of water |
2H2O electricity→ 2H2 + O2 |
|
|
Rusting of iron |
4Fe + 3O2 →2Fe2O3 |
|
|
The reaction of quicklime (CaO) with water |
CaO + H2O → Ca(OH)2 Ca(OH)2 is known as slaked lime. |
|
|
Photosynthesis |
6CO2 + 6H2O → C6H12O6 + 6O2 (reaction takes place in the presence of sunlight and chlorophyll) |
|
|
Respiration |
C6H12O6 + 6O2 → 6CO2 + 6H2O |
|
|
Combustion of hydrogen – Reaction of hydrogen gas with pure hydrogen. This is an exothermic reaction. |
2H2 + O2 → 2H2O + energy |
|
|
Decomposition of FeSO4 |
2FeSO4 +heat → Fe2O3(s) + SO2(g) + SO3(g) (Fe2O3(s) is green in color) |
|
|
Decomposition of lead nitrate – In this reaction, brown fumes of nitrogen dioxide gas are formed with the yellow coloured residue of lead oxide. |
2Pb(NO3)2 → 2PbO + 4NO2 + O2 |
|
|
Displacement reaction of iron and copper sulfate – Iron is more reactive than copper, so it displaces copper from its salt and produces iron sulfate. |
Fe + CuSO4 →FeSO4 + Cu |
This ends our coverage on a list of Various Types of Chemical Reactions. We hope you enjoyed learning and were able to grasp the concepts. We hope after reading this article you will be able to differentiate various reactions easily and it will help you in experiments as well because we have covered almost all-important chemical reactions of Class X Chemistry Experiments.
FAQ
- Combination reaction.
- Decomposition reaction.
- Displacement reaction.
- Double Displacement reaction.
- Precipitation Reaction.

